Overview
Cold rooms, walk-in freezers, and commercial refrigerated warehouses are built using modular sandwich panel systems. These constructions ensure superior insulation, hygiene, and structural efficiency to maintain the strict temperature ranges required for perishable items and pharmaceuticals.


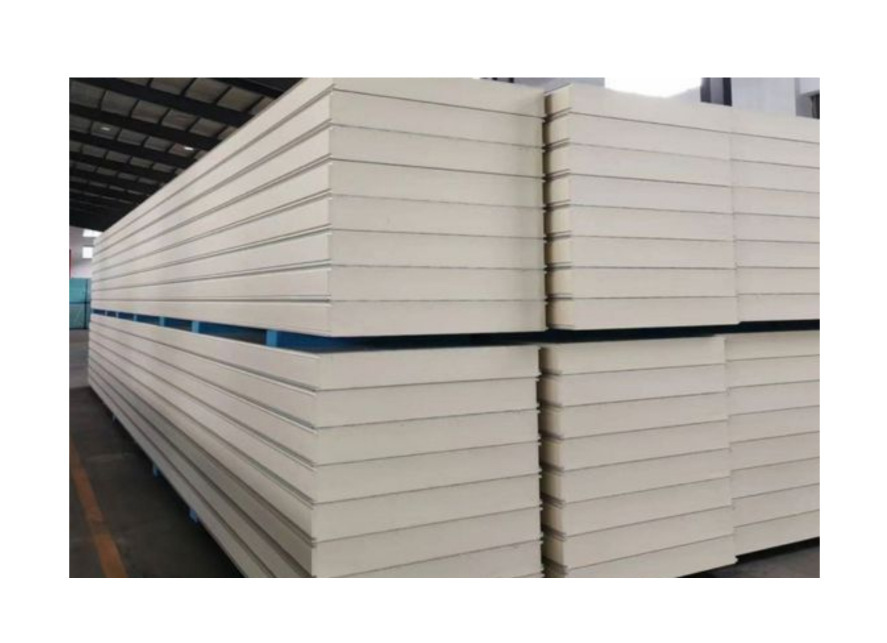
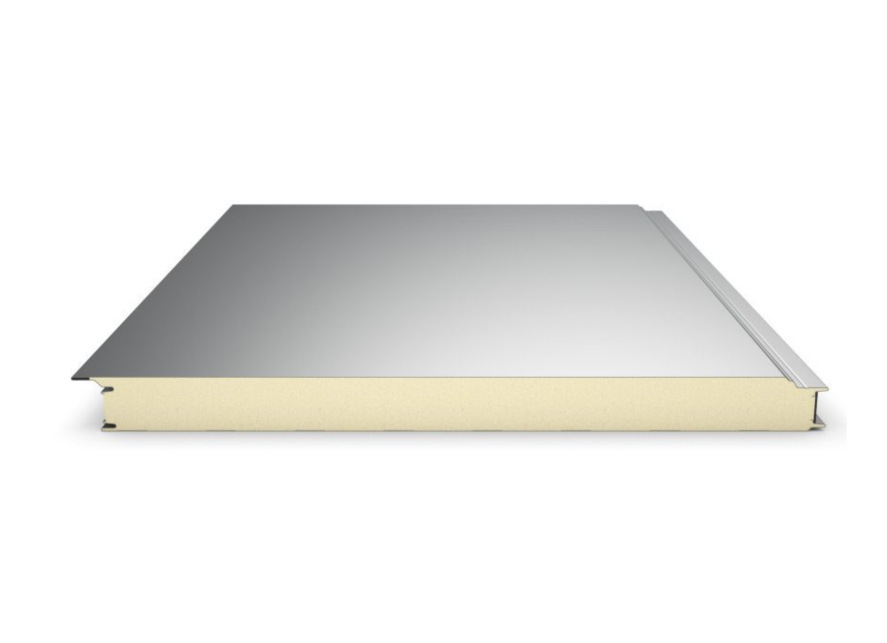
2. Sandwich Panel Specifications
Core Material: Polyurethane (PU) or PIR (Polyisocyanurate)
Thermal Conductivity: PU: 0.022–0.025 W/m·K, PIR: 0.020–0.023 W/m·K
Thickness:
- 50mm – For light chilling (10–15°C)
- 100mm – For cold rooms (0–5°C)
- 150–200mm – For freezers (-18°C or lower)
Core Density: 38–45 kg/m³
Outer Skins: PPGI, stainless steel, or PVC film‑coated GI
Joint System: Cam‑lock or tongue & groove with silicone sealing
Fire Resistance: PU (B2–B3), PIR (B1)
Surfaces: Hygienic, washable, anti‑bacterial

3. Steel Frame Structure
For large warehouses or long panel spans, the steel frame includes:
- Main Columns: H/I-beam, Q235/Q345, 150x150mm, 5–8mm thickness
- Roof Beams: C-channels/U-beams, 150x50mm or 200x60mm, 2.5–4mm
- Bracing: Angle bars or rods (50x5mm or 12mm rods)
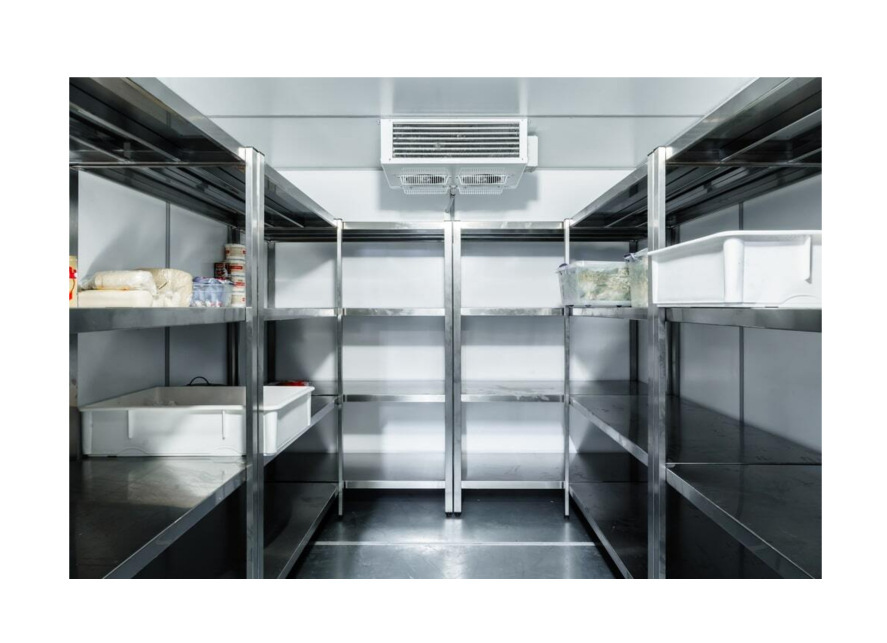
4. Flooring System
For cold rooms and freezers, the flooring system features:
- Subfloor: Reinforced concrete or metal frame
- Insulation: PU panels (50–200mm) with a vapor barrier
- Top Layer: Anti‑slip stainless steel or epoxy‑coated GI
- Drainage: Sloped floor with proper drains (heater strip for freezer use)
- Optional: Thermal break or heater cable in the subfloor

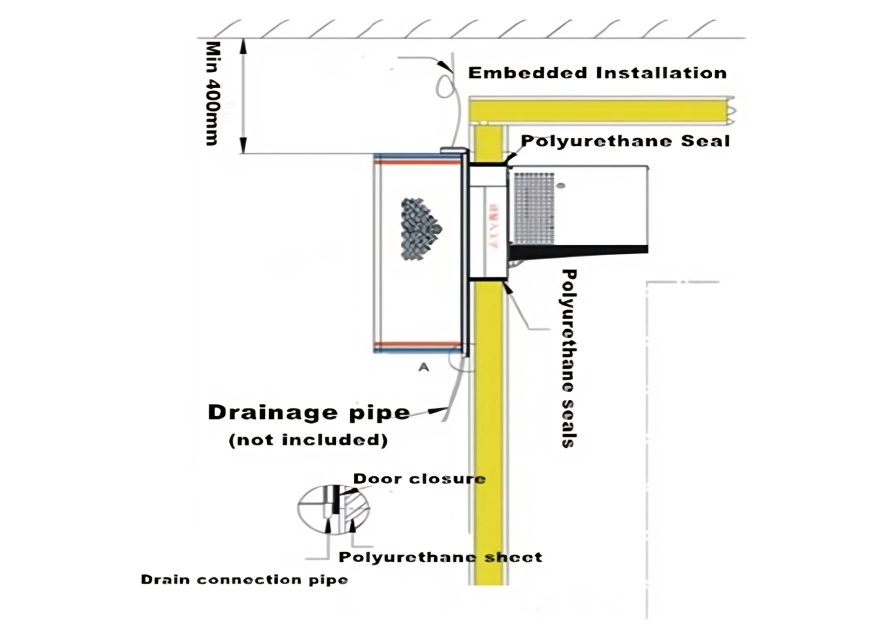
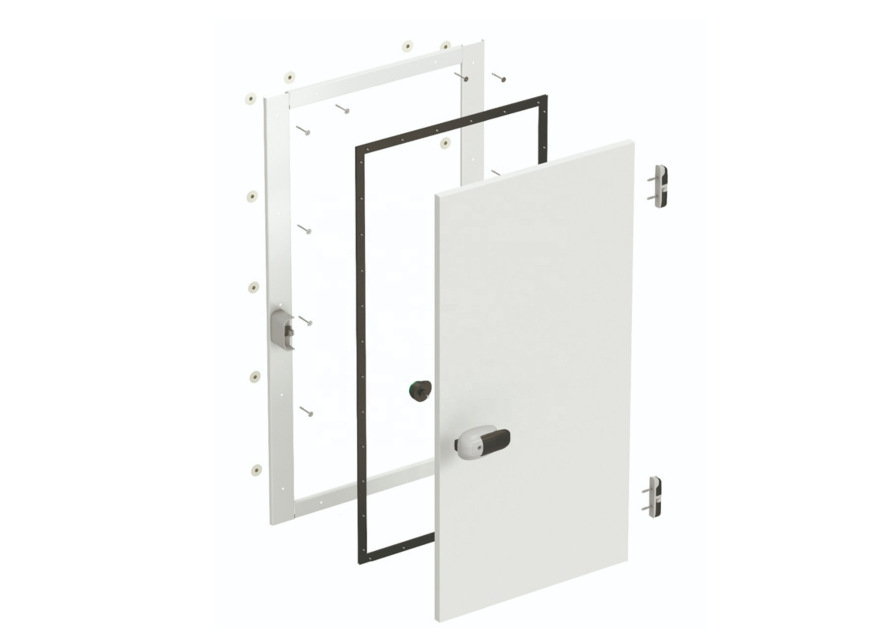
5. Cold Room Doors
Cold room doors are critical for maintaining insulation, hygiene, and operational efficiency. Options include:
- Hinged Doors: Insulated with magnetic seals for walk-in coolers/freezers.
- Sliding Doors: Suitable for larger access with manual/automatic operation.
- Swing Doors (PVC Strip): Reduce temperature exchange in high‑traffic areas.
- High‑Speed Roll‑Up Doors: For rapid cycles in logistics centers.


6. Insulation Details
Effective insulation prevents temperature fluctuations and reduces energy consumption. Key aspects:
- Insulation Material: PU or PIR panels (PIR offers better fire resistance).
- Panel Thickness: 50mm for chill rooms; 100mm for cold rooms; 150–200mm for freezers.
- Sealing Techniques: Tongue‑and‑groove or cam‑lock joints with PU foam or silicone sealant; vapor barriers are recommended in floors.
- Thermal Bridge Prevention: All mounting points and joints must be insulated or broken thermally.


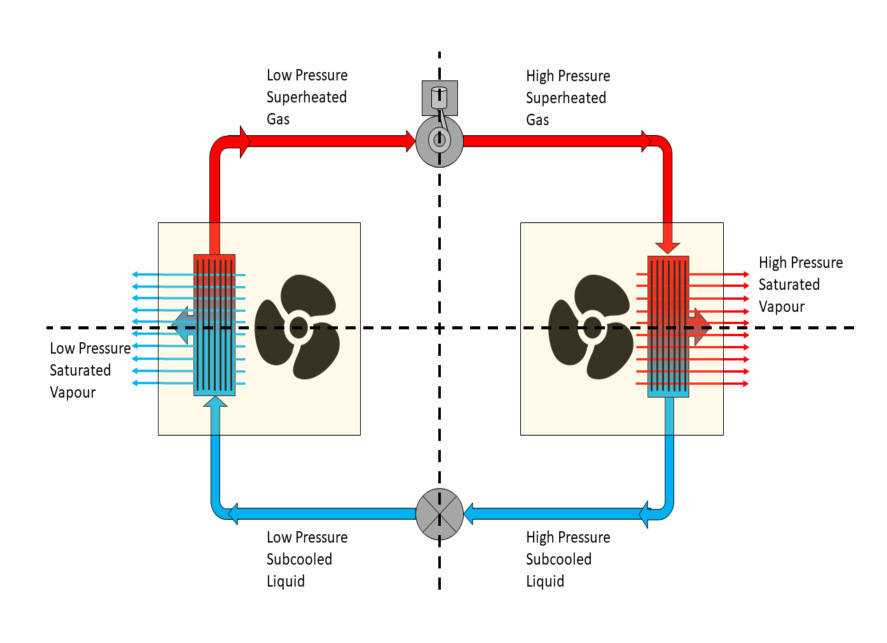
7. HVAC & Refrigeration Considerations
The refrigeration system must maintain precise temperatures and uniform airflow. Consider:
- Refrigeration Systems: Options include monoblock units, split systems, or centralized cooling plants based on facility size.
- Key Features: Precise temperature control, humidity regulation, auto‑defrosting, and backup systems for critical storage.
- Ventilation & Pressure Relief: Incorporate pressure equalization valves and design airflow for uniform cooling.